 1996-97 Mars Images from HST
1996-97 Mars Images from HST
 1996-97 Mars Images from HST
1996-97 Mars Images from HSTlast modified Page access count =
NOTE: These images are made available in order to share with the public
the excitement of new discoveries being made by the Hubble Space Telescope.
HST scientists are in the process of calibrating and validating this data.
The full digital images necessary for scientific analysis are available
as part of the
HST data archive at the
Space Telescope Science Institute.
Examine Images by Date or Type
September | October | November | December
1996 Polar Dust Storms | 1995 Opposition | 1997 Opposition
1994-1995 HST Mars Image Archive
HST Imaging of the Mars Pathfinder landing site
Journal Article: Mars Mineralogy from HST Data
MarsNet: Linking Amateur and Professional Mars Observers

Back to Menu at the top of this page


![]() October 9, 1996 Color composite, CML=45
October 9, 1996 Color composite, CML=45

![]() October 15, 1996 Color composite, CML=165
October 15, 1996 Color composite, CML=165
Back to Menu at the top of this page

Back to Menu at the top of this page

Back to Menu at the top of this page


![]() January 4, 1997 Color composite, CML=165
January 4, 1997 Color composite, CML=165
Back to Menu at the top of this page
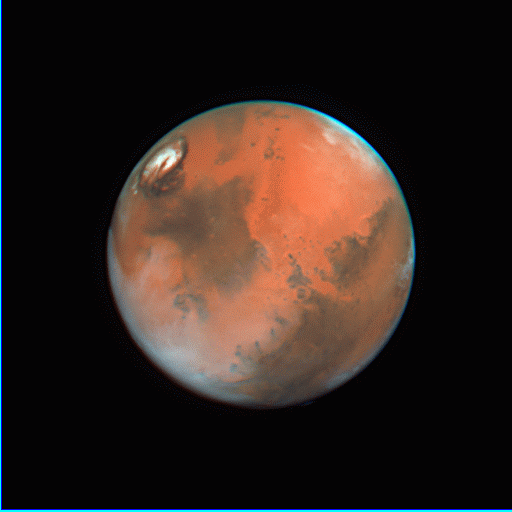

![]() March 30, 1997 Color composite, CML=105
March 30, 1997 Color composite, CML=105
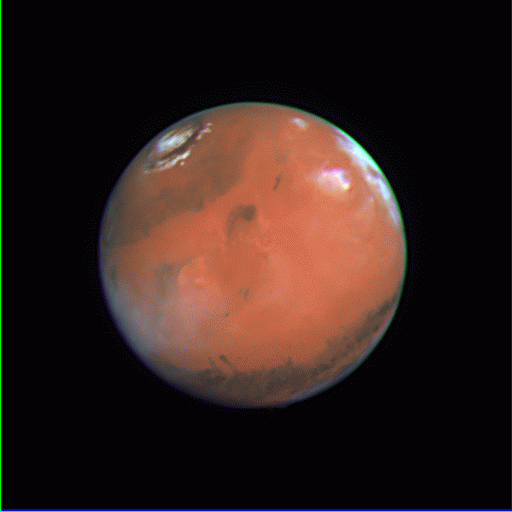
![]() March 30, 1997 Color composite, CML=195
March 30, 1997 Color composite, CML=195

![]() March 30, 1997 Color composite, CML=285
March 30, 1997 Color composite, CML=285
Back to Menu at the top of this page

Back to Menu at the top of this page
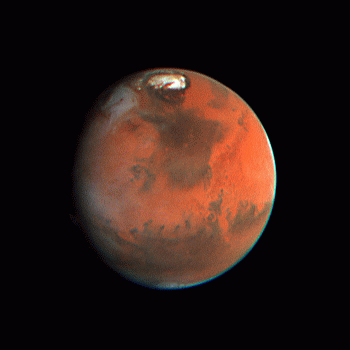

![]() May 17, 1997 Color composite, CML=165
May 17, 1997 Color composite, CML=165

![]() May 17, 1997 Color composite, CML=285
May 17, 1997 Color composite, CML=285
Back to Menu at the top of this page
Two Hubble Space Telescope images of Mars, taken about a month apart on September 18 and October 15, 1996, reveal a state-sized dust storm churning near the edge of the Martian north polar cap. The polar storm is probably a consequence of large temperature differences between the polar ice and the dark regions to the south, which are heated by the springtime sun. The increased sunlight also causes the dry ice in the polar cap to sublime and shrink.
Mars is famous for large, planet-wide dust storms. Smaller storms resembling the one seen here were observed in other regions by Viking orbiters in the late 1970s. However, this is the first time that such an event has been caught near the receding north polar cap. The Hubble images provide valuable new insights into the behavior of localized dust storms on Mars, which are typically below the resolution of ground-based telescopes. This kind of advanced planetary "weather report" will be invaluable for aiding preparation for the landing of NASA's Pathfinder spacecraft in July 1997 and the arrival of Mars Global Surveyor orbiter in September 1997.
Top (September 18, 1996) - The salmon colored notch in the white north polar cap is a 600-mile (1,000 kilometer) long storm -- nearly the width of Texas. The bright dust can also be seen over the dark surface surrounding the cap, where it is caught up in the Martian jet stream and blown easterly. The white clouds at lower latitudes are mostly associated with major Martian volcanos such as Olympus Mons. This image was taken when Mars was more than 186 million miles (300 million kilometers) from Earth, and the planet was smaller in angular size than Jupiter's Great Red Spot!
Bottom (October 15, 1996) - Though the storm has dissipated by October, a distinctive dust-colored comma-shaped feature can be seen curving across the ice cap. The shape is similar to cold fronts on Earth, which are associated with low pressure systems. Nothing quite like this feature has been seen previously either in ground-based or spacecraft observation. The snow line marking the edge of the cap receded northward by approximately 120 miles (200 kilometers), while the distance to the Red Planet narrowed to 170 million miles (275 million kilometers).
Technical notes: To help compare locations and sizes of features, map projections (right of each disk) are centered on the geographic north pole. Maps are oriented with 0 degrees longitude at the top and show meridians every 45 degrees of longitude (longitude increases clockwise); latitude circles are also shown for 40, 60, and 80 degrees north latitude. The color images were assembled from separate exposures taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2.
 Mars Polar Dust Storms seen from HST
Mars Polar Dust Storms seen from HST
Back to Menu at the top of this page
For information contact Jim Bell